We want to help you feel more informed when it comes time for furnace repair decisions. Because of that, this article explains the basics of how a furnace works. That way you can have a better idea of what a technician is talking about if your furnace stops working.
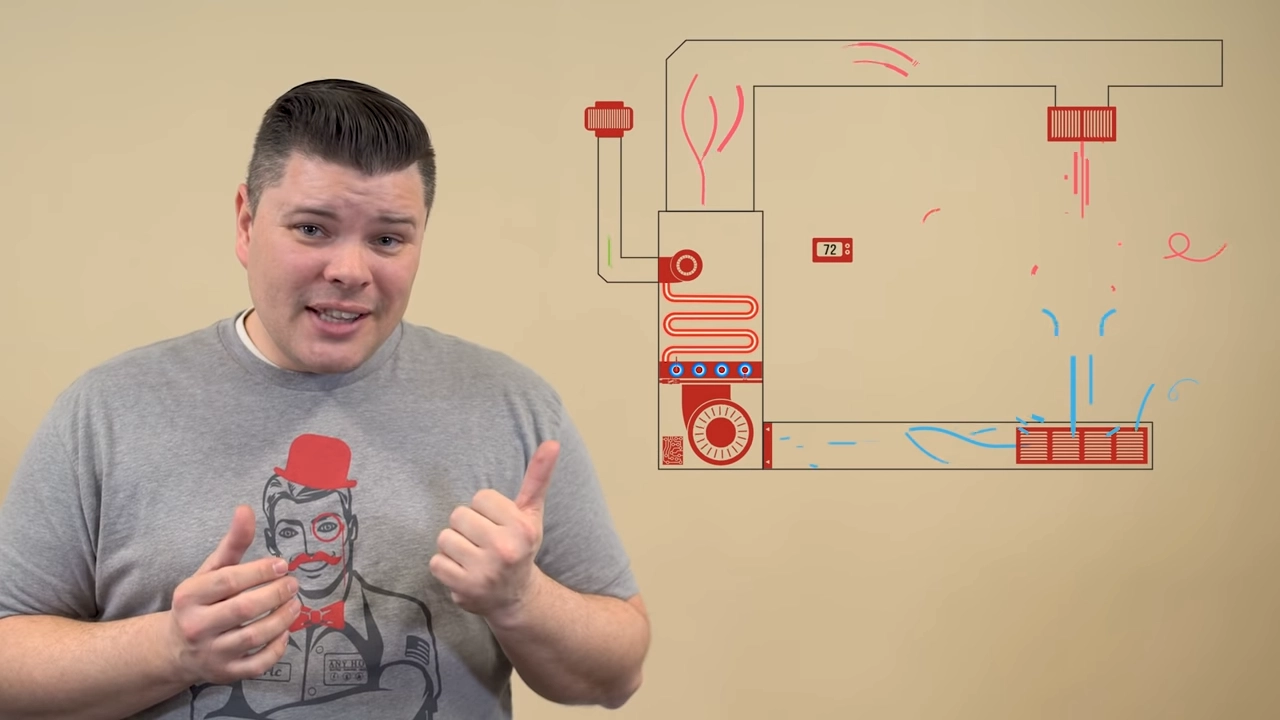
Calling For Heat and Lighting Up: The thermostat sends a signal to the circuit board calling for heat. The inducer motor turns on and draws combustion air into the furnace. This helps to make sure the gas is burning right. Next, an igniter will either glow or spark to ignite the gas that starts flowing. This gas ignites and sends hot air and noxious gasses into the heat exchanger.
Safety Measures and Heat Transfer: To make sure that the gas ignites, there’s a flame sensor that’s placed right in the path where the flame should be. If it senses a flame the heating process continues. At the same time, the hot exhaust gets drawn into the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger gets very hot, heating up the air that's flowing across it.

Removing Exhaust: While that's happening, the gas flames are letting off fumes, gases, and carbon monoxide. The heat exchanger tubes have openings on either end to catch and release that exhaust. The superheated gases travel through the heat exchanger and exit a vent outside. Now we can go back to the air that’s blowing across the heat exchanger.
Warming The Home: The blower fan pulls cool air from your home through the return vents and filter. That air travels across the heat exchanger and heats up. Then it blows through the ducting and out the supply vents. The air cools off as it warms your home. Last, the blower motor pulls it back through the return vents to repeat the cycle. It will keep going until the room is warm and the thermostat sends a signal to stop.